Cerebral angiography is a demonstrative test that utilizes X-beams. It creates a cerebral angiogram, or a picture that can assist your PCP with tracking down blockages or different anomalies in the veins in the head and neck. Blockages or anomalies can prompt a stroke or draining in the cerebrum.
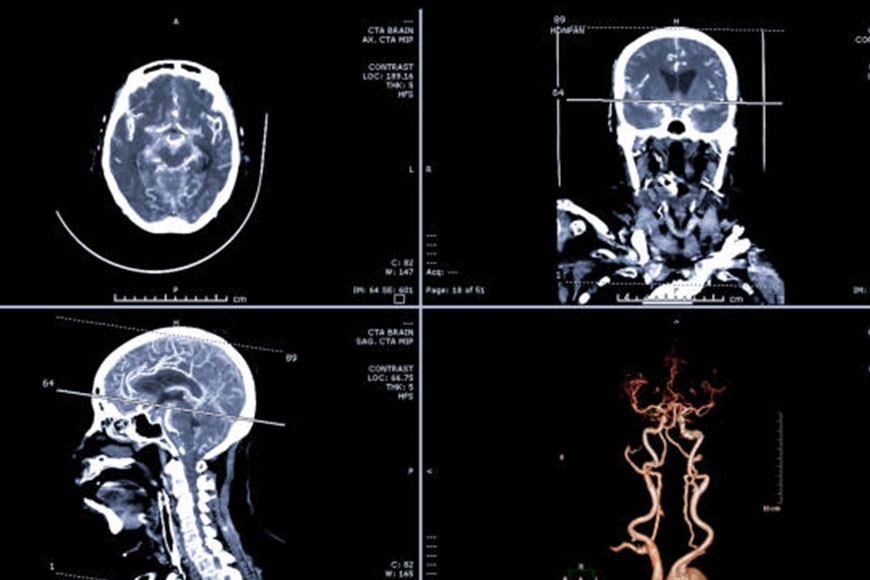
In this test, your primary care physician infuses a differentiation medium into your blood. The difference material assists the X-beams with making an unmistakable image of the veins so your PCP can recognize any blockages or anomalies.
Services
Not every person with stopped up veins needs a cerebral angiography. It’s normally possibly done in the event that your primary care physician needs more data to design your treatment after different tests. This is on the grounds that it is intrusive and conveys a few dangers.
Angiography may likewise be utilized to assist with treating a few conditions including veins in the neck and mind. Cerebral angiography can help analyze:
- aneurysm
- Arteriosclerosis
- Blood vessel venous distortions
- Vasculitis or vasculitis
- mind cancers
- blood clumps
- breaks in the coating of the course
Cerebral angiography may likewise assist your PCP with tracking down the reason for a portion of your indications, including:
- mind assault
- Extreme cerebral pain
- cognitive decline
- hazy
- Wooziness
- Obscured or twofold vision
- shortcoming or deadness
- Loss of equilibrium or coordination
Instructions to plan
Converse: with your primary care physician regarding how to plan. You will most likely be unable to eat or drink after 12 PM before the method.
Before the methodology, your PCP may likewise request that you quit taking prescriptions that can build your danger of dying. These include:
- blood thinners
- anti-inflamatory medicine
- Non-steroidal mitigating drugs
In the event that you are breastfeeding, express your milk before the technique, and don’t breastfeed your child again for no less than 24 hours. This holding up time will give the differentiation material chance to leave your body.
Alert your primary care physician
Let your primary care physician know if you have any sensitivities or ailments. Certain individuals are oversensitive to the difference material utilized during the strategy. Let your PCP know if you have any sensitivity, including aversions to sedation or difference material given for a CT filter. Your PCP might recommend hostile to sensitivity prescriptions before the test.
Certain illnesses and ailments can build the danger of inconveniences during the test. Assuming you have diabetes or kidney sickness, the difference material can make impermanent harm your kidneys. Assuming that you are pregnant or figure you may be, you ought to get some information about radiation openness during the test.
What’s in store during the activity?
Your medical services group for this test might incorporate a radiologist, neurosurgeon or nervous system specialist who spends significant time in interventional radiology and a radiology expert.
A great many people are quieted before the system. Others – particularly youngsters – are given general sedation. This is on the grounds that you must be still for the test to be powerful. The calming will assist you with feeling loose, and you might nod off.
During the method, your head will be immobilized with tape, tape, or blocks. It is vital to stay as yet during the test.
To begin, your primary care physician will disinfect a region of your crotch. They’ll embed a catheter (a long, adaptable cylinder) and string it through a vein into the carotid corridor. This is the vein in your neck that conveys blood to your cerebrum.
The difference color will course through the catheter into the supply route. From that point, it will make a trip to the veins in your mind. You might feel warm as the difference color courses through your body. Then, at that point, the specialist takes a few x-beams of the head and neck. While the sweeps are being performed, you might be approached to stay still or even pause your breathing for a couple of moments.
Then, your primary care physician will eliminate the catheter and spot a swathe over the addition site. The whole interaction for the most part requires one to three hours.
Hazards
Cerebral angiography conveys a few intriguing however genuine dangers. They include:
- Stroke (assuming the catheter slackens the plaque inside a vein)
- Vascular harm, including vein hole
- Blood clusters can conform to the tip of the catheter
- Make certain to examine all hazards cautiously with your PCP.
Follow-up after cerebral angiography
After the system, you’ll go to the recuperation room, where you’ll lie still for two to six hours prior to returning home. At home, be mindful so as not to lift weighty items or exhaust yourself for somewhere around seven days.
Call your primary care physician immediately assuming you experience any of the accompanying:
- Indications of a stroke, including slurred discourse, shortcoming, deadness, or vision issues
- Redness and expanding at the catheter inclusion site
- Expanding or frigidity in the leg or foot
- Source
Discombobulating
At the point when your outcomes are free, the radiologist will decipher them. Your primary care physician will impart these outcomes to you and talk about follow-up tests or treatment.

